# Realize One-to-One Video Calling
This guide introduces how to achieve one-to-one video calling. API call sequence for one-to-one call is as shown below:
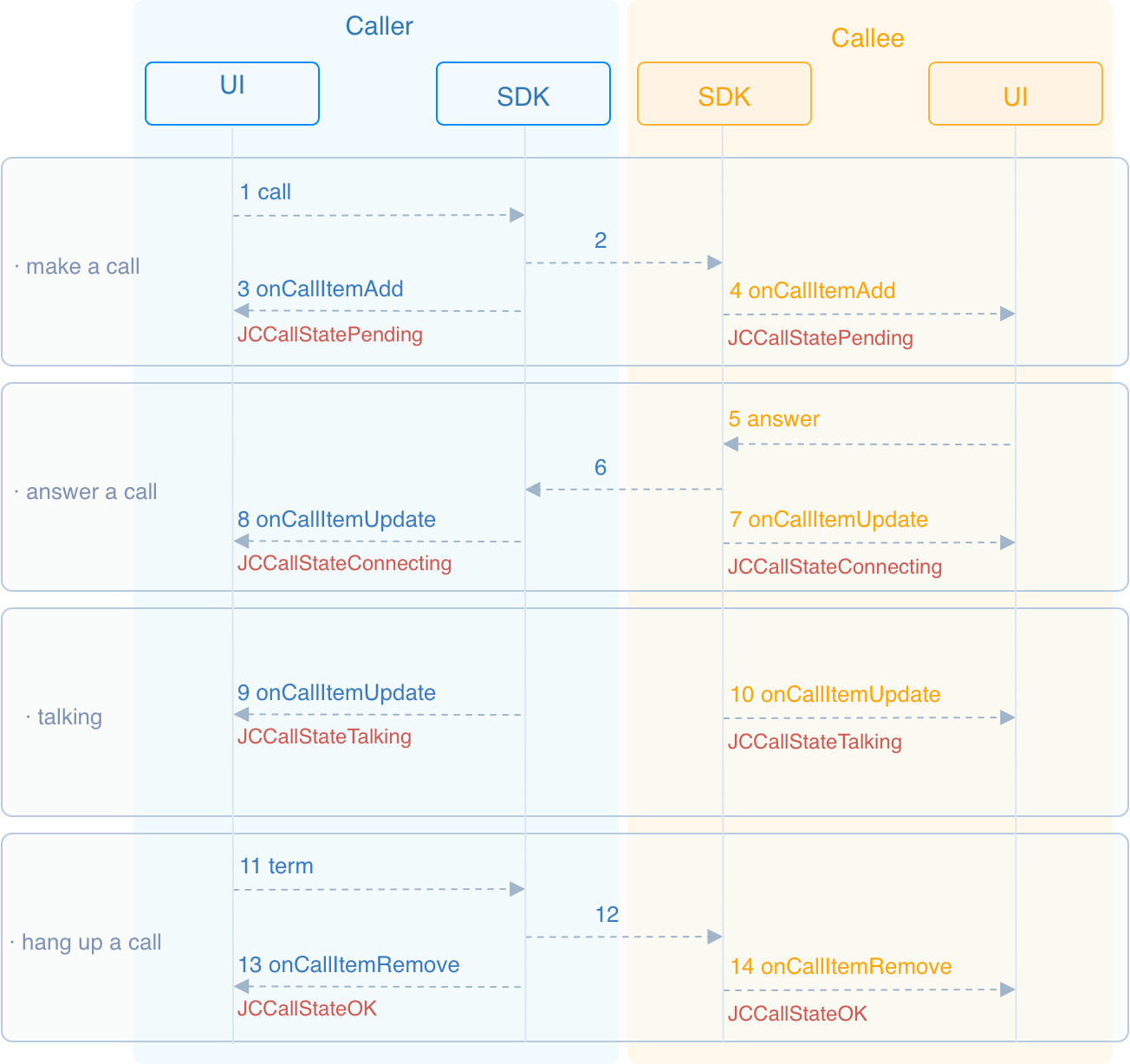
# Initialize
Call JCMediaDevice.create (opens new window) and JCCall.create (opens new window) to initialize the modules needed for one-to-one calling:
/// Create a new class and implement it
class JCManager : JCClientCallback, JCMediaDeviceCallback,JCCallCallbac{
#region JCMediaDeviceCallback
public void onCameraUpdate(){...}
public void onAudioOutputTypeChange(string audioOutputType){...}
#endregion
#region JCCallCallbac
...
/// Implement the methods in JCCallCallbac
...
#endregion
/// Declare object
JCMediaDevice mMediaDevice;
JCMediaChannel mMediaChannel;
/// Initialization function
public bool initialize(Context context) {
/// 1. Media class
mMediaDevice = JCMediaDevice.create(mClient, this);
/// 2. Call class
mCall = JCCall.create(mClient, mMediaDevice, this);
}
}
# Make a call
To call call (opens new window) to initiate a video call, the parameters to be filled are:
userIDFill in the user ID of the other party.videoSelect whether to call a video call, and true means to make a video call, while false means to make a voice call.extraParam (opens new window) is a custom pass-through string, which can be obtained through item.extraParam.
/// Initiate a voice call
mCall.call(userID, isVideo, null);
After the call is made, both the caller and the called party will receive the callback onCallItemAdd (opens new window) for the new call, and the call status will change to STATE_PENDING (opens new window) at this time. You can perform logical operations by overriding onCallItemAdd (opens new window):
public void onCallItemAdd(JCCallItem item) {
/// Business logic
if (item.direction == JCCall.DIRECTION_IN) {
/// If you are the called party
...
}else{
/// If you are the caller
...
}
}
# Create local video images
After initiating a call, call the startSelfVideo (opens new window) in the JCCallItem (opens new window) class to open the local video preview. You need to fill in the parameter JCMediaDevice.RenderType (opens new window) to select the rendering mode:
/// 1. Initiate a video call
mCall.call("222", true, null);
/// 2. Get the current active call
JCCallItem mCallItem = mCall.getActiveCallItem();
/// 3. Open the local video preview (the adaptive mode)
mCallItem.startSelfVideo(JCMediaChannel.JCMediaDeviceRenderMode.FULLAUTO);
# Answer a call
The called party receives the onCallItemAdd (opens new window) callback, and judges whether it is a video call or a voice call according to the JCCallItem (opens new window) attribute in the callback, and then makes corresponding processing:
public void onCallItemAdd(JCCallItem item) {
/// 1. If it is a video call and is ringing
if (item.direction == JCCall.DIRECTION_IN && item.video) {
/// 2. Make corresponding processing, such as "ringing" on the interface
...
}
}
Call answer (opens new window) to answer the call:
mCall.answer(item, true);
After the call is answered, the call status changes to STATE_CONNECTING.
TIP
If you want to reject the call at this time, please call the interface to hang up the call. In this case, after calling hang up, the call state changes to STATE_CANCELED.
# Create remote video images
After the called party answers the call, the two parties will establish a connection. At this time, both the caller and the called party will receive the call update callback (onCallItemUpdate), and the call status will change to STATE_TALKING.
Call startOtherVideo (opens new window) in the JCCallItem (opens new window) class to get the remote video image. The returned object is JCMediaDeviceVideoCanvas (opens new window):
public void onCallItemUpdate(JCCallItem item) {
/// If the peer is uploading a video streaming (uploadVideoStreamOther)
/// mRemoteCanvas is a JCMediaDeviceVideoCanvas object instance; please declare it before the method
if (item.state == JCCall.STATE_TALKING && mRemoteCanvas == null && item.getUploadVideoStreamOther()) {
/// Get remote video image, renderId comes from the JCCallItem object
JCMediaDeviceVideoCanvas mRemoteCanvas = item.startOtherVideo(JCMediaChannel.JCMediaDeviceRenderMode.FULLCONTENT);
...
}
}
# Hang up a call
Both the calling party and the called party can hang up the call.
Call getActiveCallItem (opens new window) to get the currently active call object:
mCall.getActiveCallItem();Call term (opens new window) to hang up the current active call:
mCall.term(item, reason, description);
Sample code:
/// 1. Get the current active call
JCCallItem item = mCall.getActiveCallItem();
/// 2. Hang up the current active call
mCall.term(item, JCCall.REASON_NONE, null);
# Destroy local and remote video images
After the call is hung up, you receive the callback onCallItemRemove (opens new window) to remove the call, and the call state changes to STATE_OK. At this time, you need to call stopSelfVideo (opens new window) and stopOtherVideo (opens new window) to destroy the local and remote video images:
public void onCallItemRemove(JCCallItem item, JCCallReason reason, String description) {
/// Destroy the local video image
item.stopSelfVideo();
/// Destroy the local video image
item.stopOtherVideo();
}

